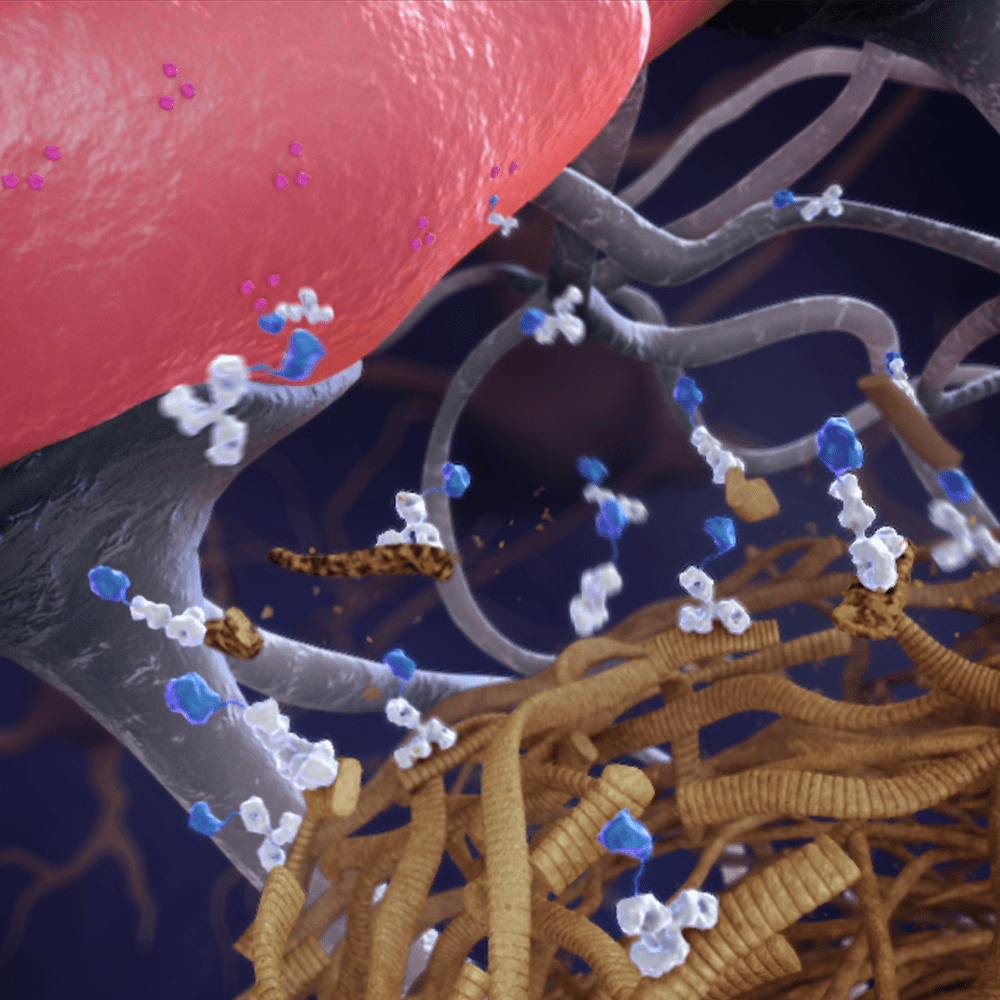
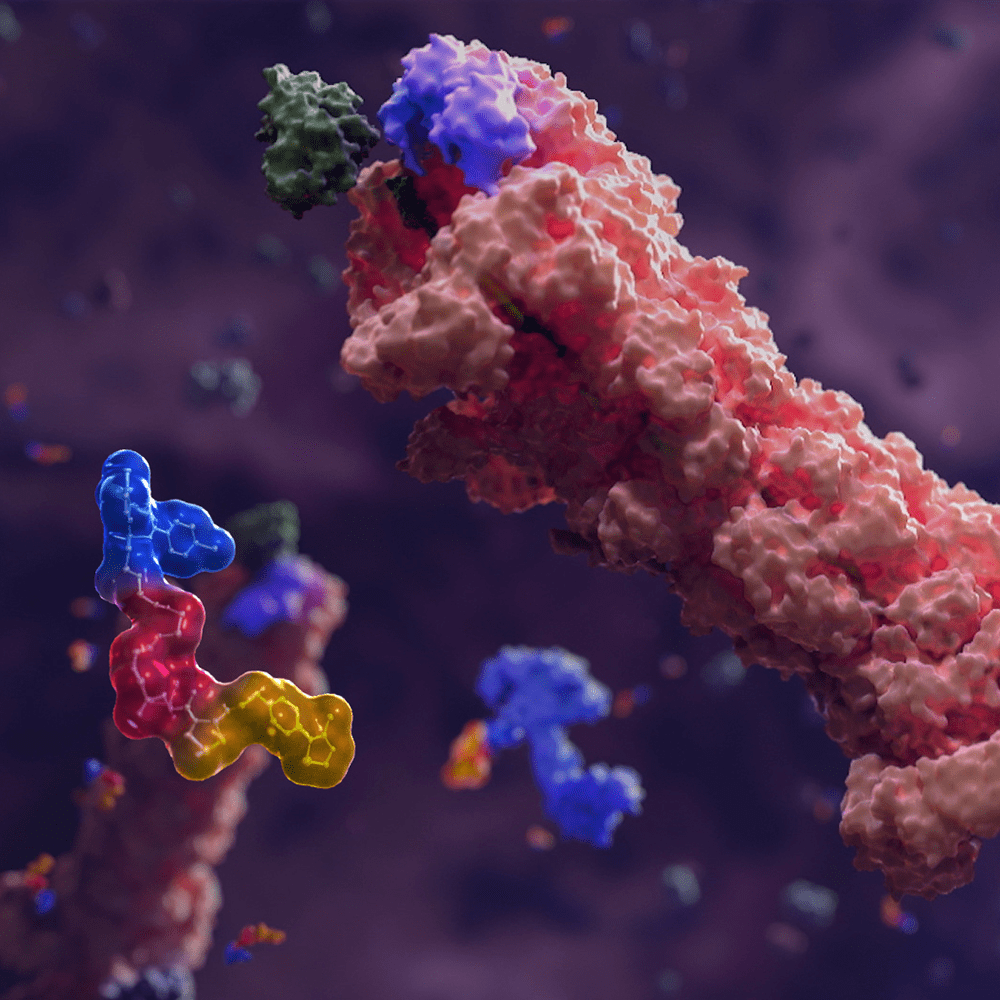Kit is a receptor tyrosine kinase that activates of a number of pathways that direct cell proliferation, survival, and apoptosis. Mutations in Kit that result in constitutive oligomerization in the absence of ligand can drive continuous oncogenic signaling.
The majority of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) cells have been found to present with overactive Kit signaling.
Gleevec, or Glivec (imatinib mesylate) competitively binds to the ATP binding pocket of both active and inactive Kit, preventing downstream signaling. Kit inhibition by imatinib may induce both apoptosis and quiescence in KIT+ GIST cells.
Related Animations