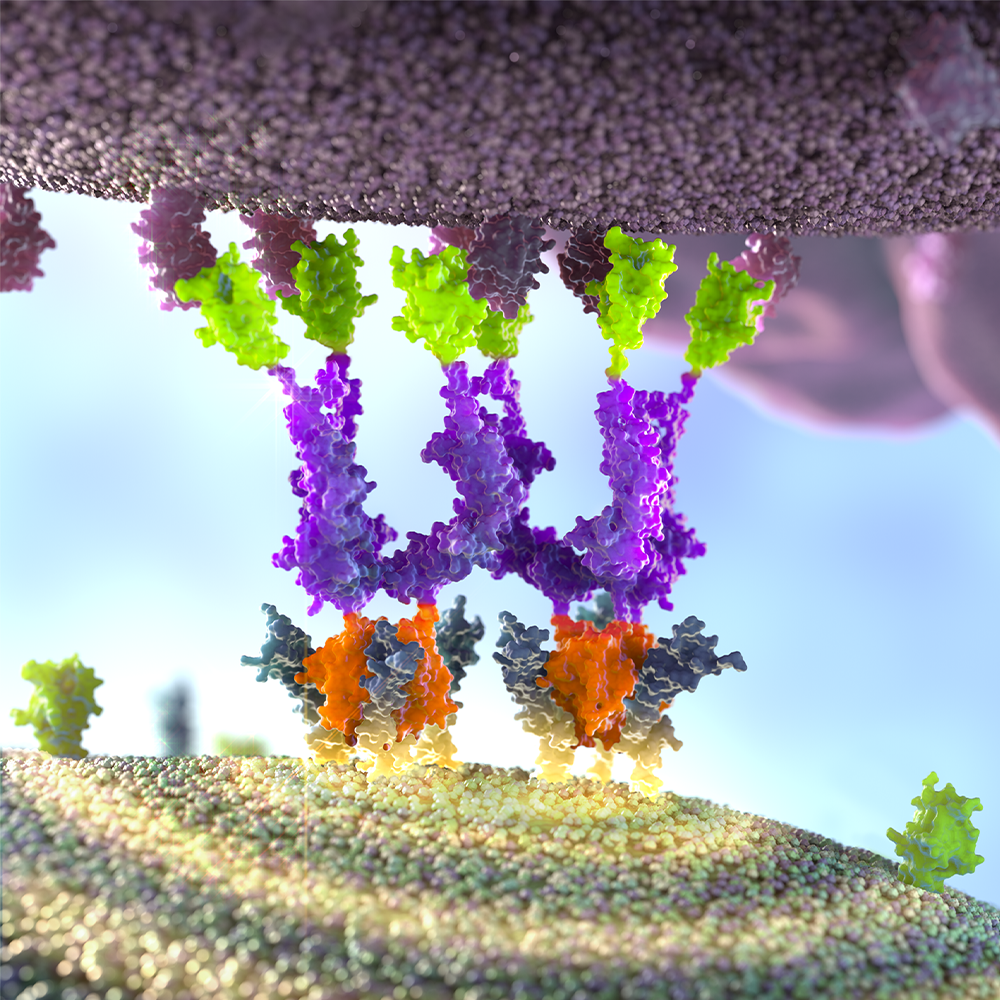
Iconic Therapeutics requested 3 illustrations depicting the structure and function of tissue factor in the human body and disease. Tissue factor is a naturally-occurring molecule in the body that is well known for its important role in blood coagulation, but it is also involved in angiogenesis, as well as cell survival and migration.
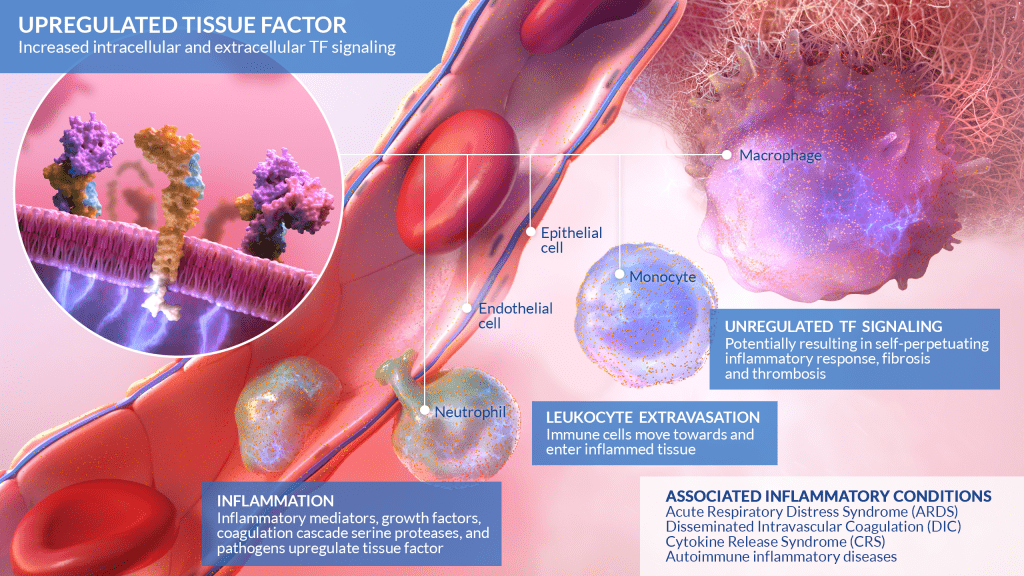
Tissue factor is a membrane-bound protein that participates in intracellular as well as extracellular signaling. In some diseases, tissue factor is overexpressed, leading to an increase in intracellular and/or extracellular signaling, which can cause inflammation and undesirable angiogenesis. Tissue factor upregulation is implicated in conditions such as acute respiratory distress syndrome and cytokine release syndrome.
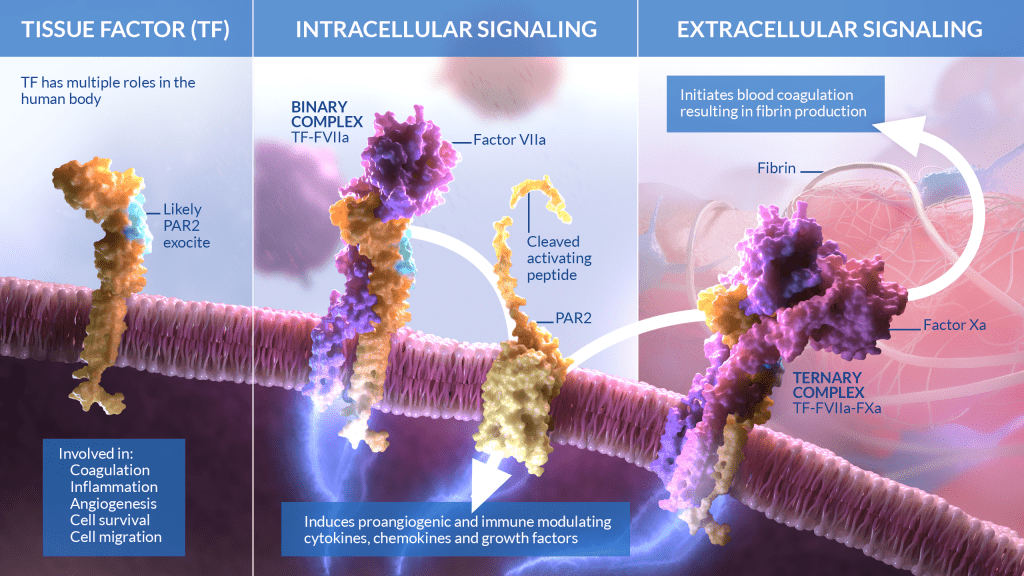
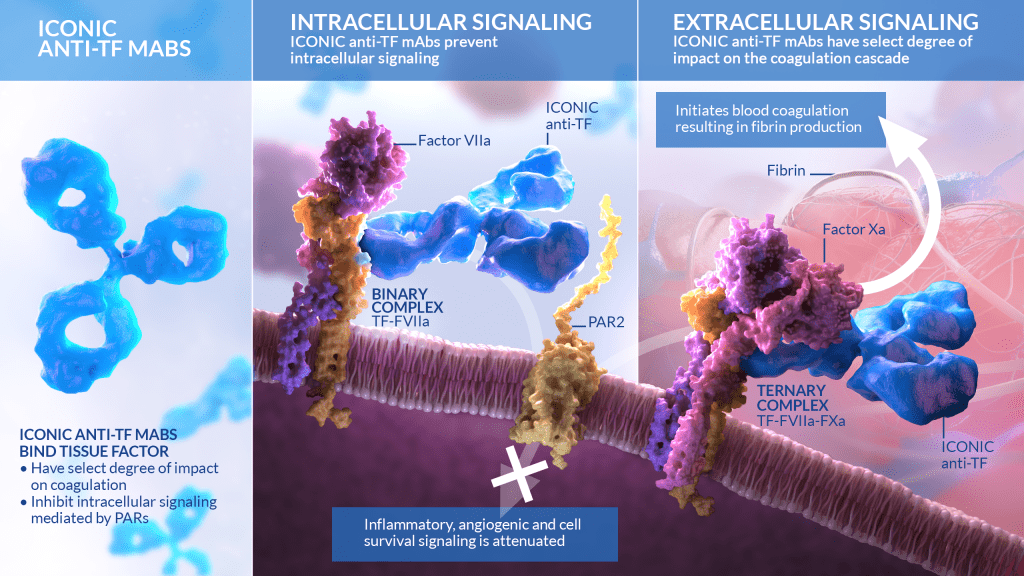
To counteract upregulated tissue factor in disease, Iconic Therapeutics has engineered a monoclonal antibody, ICON-1, against tissue factor. When the anti-TF antibody is bound, it reduces the intracellular signaling that is involved in angiogenic and inflammatory responses, while having a minimal effect on the extracellular signaling involved in the coagulation cascade.
Related Illustrations